The Temperate Deciduous Forest Biome Map provides an in-depth exploration of this captivating ecosystem, delving into its defining characteristics, global distribution, climate, vegetation, and ecological processes.
This comprehensive guide unravels the intricate tapestry of temperate deciduous forests, showcasing their unique adaptations, diverse flora and fauna, and the interplay of natural forces that shape this vibrant ecosystem.
Temperate Deciduous Forest Biome

Temperate deciduous forests are terrestrial ecosystems characterized by distinct seasonal changes and the presence of deciduous trees, which shed their leaves annually. These forests play a vital role in global biodiversity and provide numerous ecological services.
Geographical Distribution
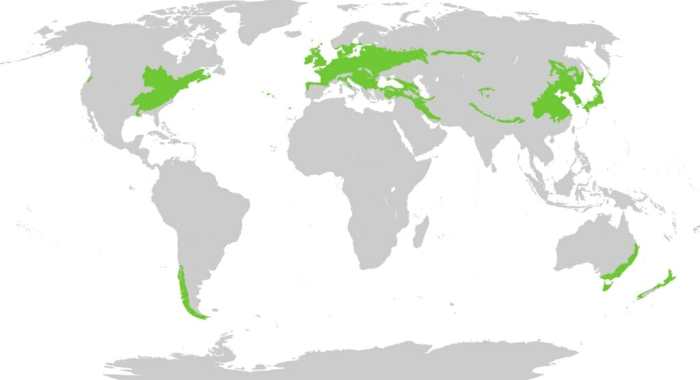
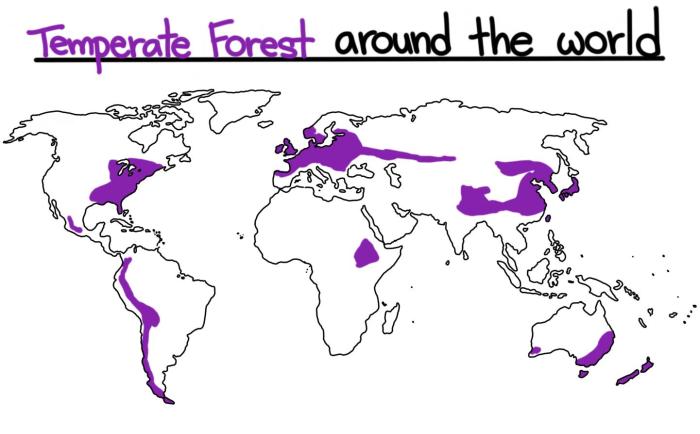
Temperate deciduous forests are found in the mid-latitudes of the Northern Hemisphere, primarily in North America, Europe, and Asia. They occur in regions with moderate climates, characterized by warm summers and cold winters, and ample precipitation throughout the year.
Climate and Vegetation
Temperate deciduous forests experience a wide range of temperatures, with average summer temperatures ranging from 15 to 25°C and winter temperatures dropping below freezing. Precipitation is typically evenly distributed throughout the year, with annual rainfall ranging from 750 to 1,500 mm.
The dominant tree species in temperate deciduous forests are broadleaf trees, such as oak, maple, beech, and birch. These trees have evolved to withstand seasonal changes, shedding their leaves in autumn to conserve water and energy during the cold winter months.
Flora and Fauna
Temperate deciduous forests support a diverse range of plant and animal species. The understory vegetation is often dominated by shrubs, herbs, and ferns, which provide habitat and food for a variety of insects, birds, and mammals.
Common animal species include deer, squirrels, rabbits, foxes, and owls. These animals have adapted to the seasonal changes in food availability and temperature by developing strategies such as hibernation, migration, and caching.
Ecological Processes
Temperate deciduous forests are characterized by a number of key ecological processes, including:
- Nutrient cycling: Nutrients are released into the soil through the decomposition of organic matter, and then absorbed by plants.
- Decomposition: Bacteria and fungi play a crucial role in breaking down dead plant and animal material, releasing nutrients back into the ecosystem.
- Energy flow: Solar energy is captured by plants through photosynthesis and transferred through the food chain to other organisms.
Fire and Disturbances, Temperate deciduous forest biome map
Fire plays a significant role in shaping temperate deciduous forests. Natural fires can occur due to lightning strikes or human activities, and they can help to clear out deadwood, promote new plant growth, and maintain the health of the forest ecosystem.
Other disturbances, such as storms and insect outbreaks, can also impact temperate deciduous forests. These disturbances can create gaps in the canopy, allowing sunlight to reach the forest floor and promote the growth of new vegetation.
FAQ: Temperate Deciduous Forest Biome Map
What is a temperate deciduous forest?
A temperate deciduous forest is a forest ecosystem characterized by trees that shed their leaves seasonally, typically during the autumn or winter.
Where are temperate deciduous forests found?
Temperate deciduous forests are found in regions with moderate climates, such as eastern North America, Europe, and parts of Asia.
What are the dominant tree species in temperate deciduous forests?
Common tree species include oak, maple, beech, and birch.