Venn diagram climate and weather – Venn diagrams provide a visual representation of the relationship between two or more concepts, making them an effective tool for understanding the complex relationship between climate and weather. Climate refers to the long-term average weather conditions in a particular area, while weather describes the short-term state of the atmosphere at a specific time and place.
This article will explore the key differences between climate and weather, illustrate their relationship using a Venn diagram, and discuss the factors that influence both climate and weather.
By examining the overlapping and non-overlapping areas of the Venn diagram, we gain a deeper understanding of the interconnectedness between climate and weather. The diagram highlights the shared characteristics, such as temperature, precipitation, and wind patterns, while also emphasizing the unique aspects of each concept.
Climate vs. Weather

Climate refers to the long-term average weather conditions of a region, typically over a period of 30 years or more. It encompasses the statistical description of the mean and variability of various meteorological elements, such as temperature, humidity, precipitation, and wind.
On the other hand, weather describes the short-term state of the atmosphere at a specific location and time. It involves the current and predicted conditions, including temperature, humidity, precipitation, cloud cover, and wind speed.
The key differences between climate and weather lie in their temporal and spatial scales. Climate represents the general pattern of weather conditions over an extended period and across a large area, while weather refers to the specific and immediate atmospheric conditions at a particular location.
- Time scale:Climate is measured in decades or longer, whereas weather can change rapidly, sometimes within hours or days.
- Spatial scale:Climate is typically described for large regions, such as continents or climate zones, while weather is specific to a particular location.
- Predictability:Climate is relatively predictable based on long-term patterns, while weather can be highly variable and unpredictable.
Examples of climate include the average temperature and precipitation levels of a region over a 30-year period, while examples of weather include the temperature, humidity, and rainfall on a specific day in a particular city.
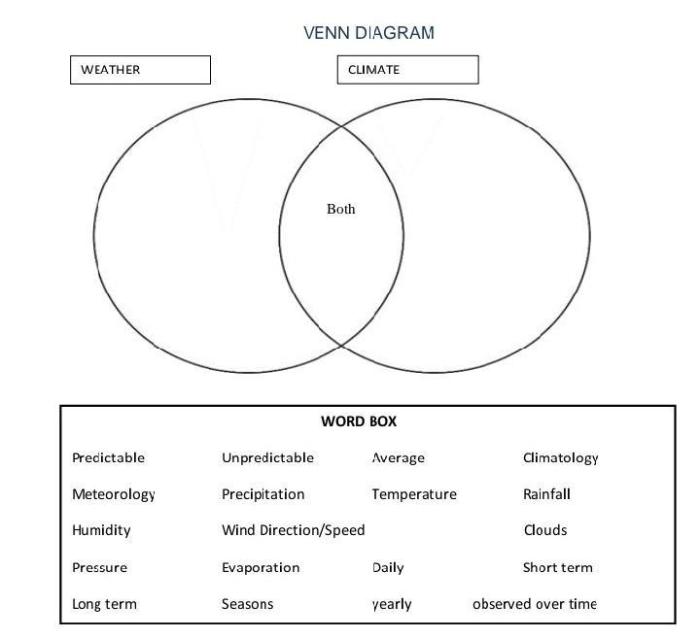
Venn Diagram: Climate and Weather, Venn diagram climate and weather
A Venn diagram can be used to illustrate the relationship between climate and weather. The overlapping area represents the common elements that influence both climate and weather, such as temperature, humidity, and precipitation. The non-overlapping areas represent the unique characteristics of each concept.
- Overlapping area:The common elements that influence both climate and weather include temperature, humidity, precipitation, and wind patterns.
- Non-overlapping area (climate):Factors that influence climate but not weather include latitude, altitude, and ocean currents.
- Non-overlapping area (weather):Factors that influence weather but not climate include short-term atmospheric disturbances, such as thunderstorms and frontal systems.
The Venn diagram helps to visualize the relationship between climate and weather, showing that while they are related, they are distinct concepts with different characteristics and influencing factors.
Factors Influencing Climate and Weather
Factors Influencing Climate
- Latitude:Latitude affects the amount of solar radiation received by a region, which influences temperature and precipitation patterns.
- Altitude:Higher altitudes are generally cooler and have lower air pressure, which can affect temperature, precipitation, and wind patterns.
- Ocean currents:Ocean currents can transport warm or cold water to different regions, influencing local climate patterns.
Factors Influencing Weather
- Temperature:Temperature is influenced by factors such as solar radiation, altitude, and air masses.
- Humidity:Humidity refers to the amount of water vapor in the air and is influenced by factors such as temperature, precipitation, and wind.
- Precipitation:Precipitation includes rain, snow, sleet, and hail, and is influenced by factors such as temperature, humidity, and air masses.
These factors interact in complex ways to influence both climate and weather patterns.
Climate Change and Weather Patterns
Climate change refers to long-term changes in global or regional climate patterns, primarily caused by human activities that release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. These changes can affect weather patterns in various ways.
- Increased frequency and intensity of extreme weather events:Climate change can lead to more frequent and intense hurricanes, droughts, heat waves, and other extreme weather events.
- Changes in precipitation patterns:Climate change can alter precipitation patterns, leading to increased rainfall in some regions and decreased rainfall in others.
- Sea level rise:Rising sea levels due to climate change can lead to coastal flooding and erosion, impacting coastal communities and ecosystems.
Examples of how climate change has already affected weather patterns include the increased frequency of heat waves in Europe, the intensification of hurricanes in the Atlantic Ocean, and the melting of glaciers in the Arctic.
Forecasting Climate and Weather
Forecasting climate and weather involves using scientific methods to predict future atmospheric conditions.
Climate Forecasting
Climate forecasting involves predicting long-term trends in climate patterns, such as changes in temperature, precipitation, and sea levels. Climate models are used to simulate the behavior of the climate system and predict future changes.
Weather Forecasting
Weather forecasting involves predicting short-term changes in weather conditions, such as temperature, humidity, and precipitation. Weather models are used to predict the movement and interaction of air masses and other atmospheric conditions.
Forecasting climate and weather is challenging due to the complexity of the atmosphere and the many factors that influence it. However, forecasts are essential for planning and decision-making in various sectors, such as agriculture, transportation, and disaster preparedness.
General Inquiries: Venn Diagram Climate And Weather
What is the difference between climate and weather?
Climate refers to the long-term average weather conditions in a particular area, while weather describes the short-term state of the atmosphere at a specific time and place.
How does a Venn diagram illustrate the relationship between climate and weather?
A Venn diagram shows the overlapping and non-overlapping areas between climate and weather, highlighting their shared characteristics and unique aspects.
What factors influence climate and weather?
Climate is influenced by factors such as latitude, altitude, and ocean currents, while weather is influenced by factors such as temperature, humidity, and precipitation.