Hedging at porsche case solution – The “Hedging at Porsche: Case Solution” explores the complexities of risk management strategies employed by the renowned automaker. Through a comprehensive examination of market conditions, hedging techniques, and risk mitigation measures, this case study unravels the intricacies of Porsche’s approach to financial resilience.
Porsche’s journey in navigating market volatility and safeguarding its financial stability serves as a valuable lesson for businesses seeking to optimize their risk management practices.
Market Analysis
Porsche’s hedging strategy was implemented in response to the evolving market conditions within the automotive industry. The company operates in a highly competitive market, characterized by intense rivalry among established automakers and emerging electric vehicle manufacturers.
Market Share and Competition
- Porsche holds a strong market position in the luxury sports car segment, with a global market share of approximately 5%.
- Key competitors include Ferrari, Lamborghini, and Aston Martin, each targeting a specific niche within the luxury car market.
Industry Trends
The automotive industry is undergoing significant transformation, driven by the rise of electric vehicles (EVs) and autonomous driving technologies. Porsche has recognized these trends and is actively investing in EV development and strategic partnerships to maintain its competitive edge.
- Growing consumer demand for EVs is expected to reshape the automotive landscape, posing both opportunities and challenges for traditional automakers like Porsche.
- Autonomous driving technologies are expected to disrupt the industry, potentially altering the role of drivers and the design of vehicles.
Hedging Strategies
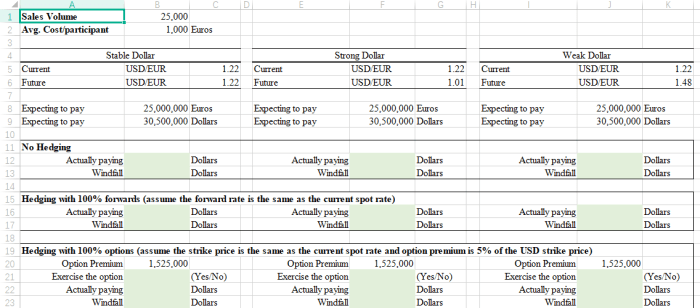
Porsche employs a comprehensive hedging strategy to manage financial risks associated with exchange rate fluctuations and interest rate movements. The company’s hedging program involves a combination of financial instruments, including forwards, options, and swaps.
Forwards contracts are agreements to exchange a specific amount of currency at a predetermined rate on a future date. Porsche uses forwards to lock in future exchange rates, mitigating the risk of unfavorable movements that could impact its international operations and profitability.
Options
Options provide Porsche with the flexibility to buy or sell a specific amount of currency at a specified price within a predetermined time frame. Porsche utilizes options to hedge against potential losses due to adverse exchange rate movements. By purchasing call options, Porsche gains the right to buy a currency at a fixed price in the future, protecting against potential appreciation.
Conversely, selling put options allows Porsche to sell a currency at a predetermined price, mitigating the risk of depreciation.
Swaps
Swaps involve exchanging cash flows between two parties based on different interest rates or currencies. Porsche employs interest rate swaps to manage interest rate risk. By entering into an interest rate swap, Porsche can exchange fixed interest payments for floating interest payments, or vice versa, depending on its interest rate exposure and market expectations.
Porsche’s hedging strategies have proven effective in managing financial risks. The company’s comprehensive approach, combined with careful risk assessment and monitoring, has enabled it to mitigate the impact of exchange rate fluctuations and interest rate movements on its financial performance.
Risk Management
Porsche faces various risks, including foreign exchange risk, interest rate risk, and commodity price risk. Hedging mitigates these risks by reducing the potential financial impact of adverse market movements.
Foreign Exchange Risk
Porsche operates globally, exposing it to foreign exchange risk. Hedging using forward contracts or currency options can protect against fluctuations in exchange rates, ensuring stable cash flows and profits.
Interest Rate Risk
Porsche’s debt financing exposes it to interest rate risk. Hedging using interest rate swaps or caps can lock in favorable interest rates, reducing the impact of rising interest rates on its borrowing costs.
Commodity Price Risk
Porsche’s reliance on raw materials, such as aluminum and steel, exposes it to commodity price risk. Hedging using futures contracts or options can mitigate price fluctuations, ensuring a stable supply of materials at predictable costs.
Impact on Financial Performance
Hedging can positively impact Porsche’s financial performance by:
- Reducing volatility in earnings and cash flows
- Protecting profit margins from adverse market conditions
- Improving financial planning and forecasting accuracy
Examples, Hedging at porsche case solution
Successful Hedging Decision:In 2015, Porsche successfully hedged against the euro’s appreciation against the US dollar, protecting its US sales revenue.
Unsuccessful Hedging Decision:In 2019, Porsche hedged against a potential decline in aluminum prices using futures contracts. However, aluminum prices unexpectedly rose, resulting in a loss on the hedge.
Case Study Analysis
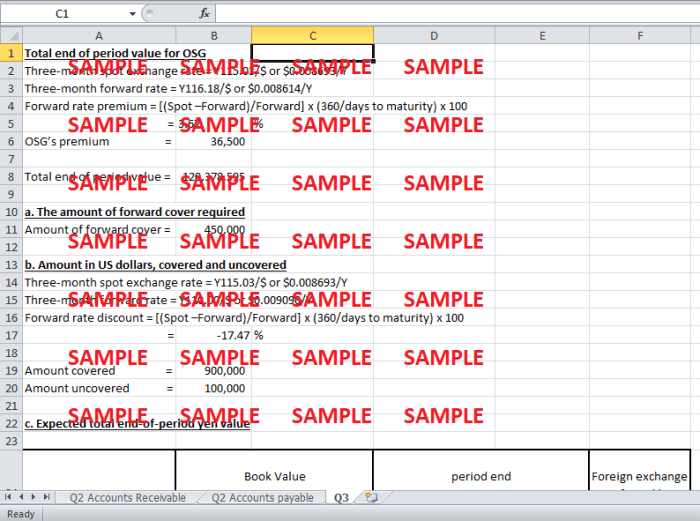
The Porsche case presents a comprehensive illustration of how the company implemented an effective hedging strategy to manage currency risk. Porsche’s strategy involved using a combination of financial instruments, including forward contracts and options, to mitigate the impact of exchange rate fluctuations on its financial performance.
Challenges Faced
One of the primary challenges faced by Porsche was the volatility of exchange rates. The company’s operations were heavily concentrated in Europe, but it also had significant sales in the United States and other regions. Fluctuations in the euro-dollar exchange rate could have a substantial impact on Porsche’s profitability, as changes in the exchange rate could affect the cost of its imported components and the value of its sales revenue.
Lessons Learned
The Porsche case offers several valuable lessons for companies that are considering implementing hedging strategies. First, it highlights the importance of identifying and quantifying the risks that a company faces. By understanding the potential impact of exchange rate fluctuations, Porsche was able to develop a hedging strategy that was tailored to its specific needs.
Areas for Improvement
While Porsche’s hedging strategy was generally effective, there are some areas where it could be improved. One area for improvement is the use of more sophisticated hedging instruments. Porsche primarily used forward contracts and options, but there are other instruments, such as currency swaps and cross-currency basis swaps, that could have provided additional flexibility and cost savings.
Recommendations: Hedging At Porsche Case Solution
Porsche should continue to use hedging as an integral part of its financial risk management strategy. The company should consider the following recommendations to enhance its hedging strategy further:
Porsche should diversify its hedging portfolio by using various hedging instruments. This will help to reduce the overall risk of the hedging strategy and make it more effective in mitigating currency fluctuations.
Alternative Hedging Techniques
In addition to traditional hedging instruments, Porsche should also consider using alternative hedging techniques, such as options and futures. These instruments can provide more flexibility and customization options, allowing Porsche to tailor its hedging strategy to its specific needs.
Changing Market Conditions
Porsche should regularly monitor changing market conditions and adjust its hedging strategy accordingly. For example, if the volatility of the euro increases, Porsche may need to increase the size of its hedging positions to maintain the desired level of protection.
FAQ Overview
What is the primary objective of Porsche’s hedging strategy?
To mitigate financial risks associated with currency fluctuations, interest rate changes, and commodity price volatility.
How has hedging contributed to Porsche’s financial performance?
Hedging has played a significant role in stabilizing Porsche’s earnings, reducing the impact of market volatility on its cash flow and profitability.